The Rise and Fall of Silicon Valley Bank: A Deep Dive into the Biggest Bank Failure Since 2008
The Rise and Fall of Silicon Valley Bank: A Deep Dive into the Biggest Bank Failure Since 2008
Silicon Valley Bank recently made headlines as the largest bank failure since the 2008 financial crisis. This blog explores the intricate details behind its downfall, focusing on its unique position in the tech community and the missteps that led to its dramatic collapse.
🌉 Introduction to Silicon Valley Bank
Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) has been a cornerstone for startups and tech companies, providing essential banking services tailored for innovation. Founded in 1983, SVB became synonymous with the tech industry, offering loans, treasury services, and investment banking to emerging companies in Silicon Valley and beyond.
Its unique focus on the tech sector allowed it to cultivate strong relationships with venture capitalists and entrepreneurs. This specialization not only fueled its growth but also made it vulnerable to the fluctuations within the tech industry. As the tech sector flourished, so did SVB, becoming a key player in the financing of new ventures and groundbreaking technologies.

Key Services Offered
- Venture Capital Financing: SVB was known for its deep ties with venture capital firms, facilitating funding for startups.
- Commercial Banking: It provided traditional banking services, such as loans and deposit accounts, tailored specifically for tech companies.
- Investment Banking: SVB offered advisory services for mergers and acquisitions, helping companies navigate complex financial landscapes.
📉 The Context of the Collapse
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank was not an isolated incident but rather a culmination of several factors. The bank’s unique position in the tech sector made it susceptible to the rapid changes in market conditions. As interest rates began to rise, SVB found itself in a precarious situation.
Many of its long-term investments were tied up in government bonds and securities, which, while generally safe, became less favorable as interest rates increased. This mismatch between assets and liabilities created significant pressure on the bank’s financial health.
Understanding the Environment
SVB's customer base was primarily composed of tech startups that thrived during periods of low-interest rates. As these rates increased, investors sought safer, higher-yielding alternatives, leading to decreased funding for startups. This shift caused a drop in deposits, further exacerbating SVB's financial woes.
💰 Understanding Banking Risks
At its core, banking is about managing risks. Banks like Silicon Valley Bank take deposits and turn them into long-term investments. This practice inherently involves risks, primarily liquidity risk—the risk that a bank cannot meet its short-term financial obligations.

Liquidity Risk Explained
- Deposit Withdrawals: If a significant number of customers withdraw their deposits simultaneously, the bank may not have enough liquid assets to meet these demands.
- Long-term Investments: By investing heavily in long-term securities, SVB locked away funds that could have been used to satisfy immediate withdrawal requests.
📉 Investment Misjudgments
SVB's investment strategy was heavily focused on long-term securities. While this approach is typically safe, it became a liability as interest rates rose sharply. The bank misjudged the potential impacts of this rapid increase, leading to significant losses.
Investors began to pull back from risky ventures, seeking stability. This shift not only reduced SVB's deposits but also highlighted the bank's overexposure to long-term investments.
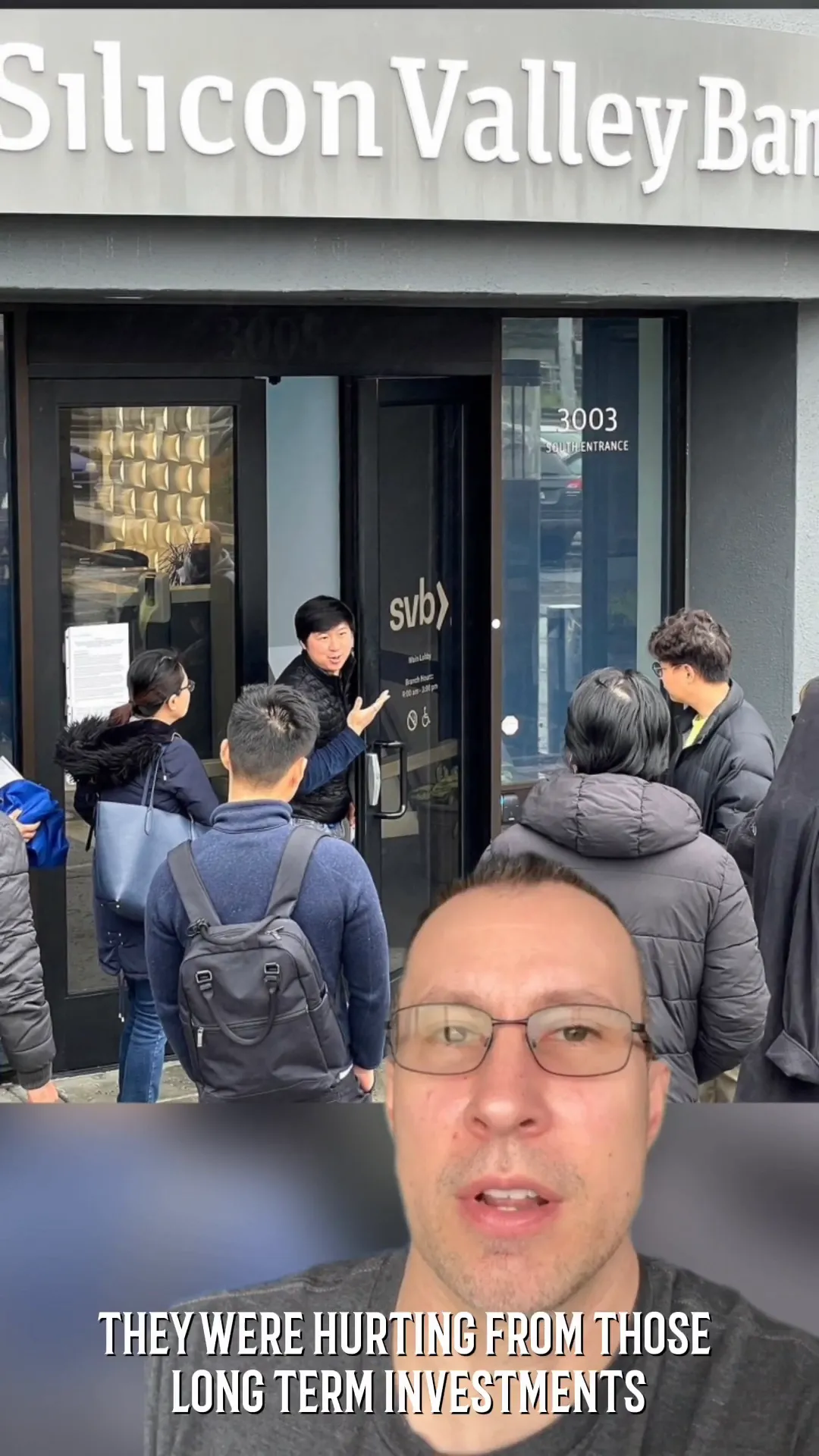

Consequences of Poor Investment Decisions
- Asset Devaluation: As interest rates increased, the value of SVB's long-term bonds decreased, impacting its balance sheet.
- Declining Deposits: With fewer startups receiving funding, deposits dwindled, creating a liquidity crisis.
📈 Impact of Rising Interest Rates
The rise in interest rates had a profound effect on Silicon Valley Bank. Initially, low-interest rates spurred growth in the tech sector, with investors eager to finance innovative startups. However, as rates climbed, that enthusiasm waned.
Higher interest rates made traditional investments more appealing, leading to a shift in investor behavior. Startups found it increasingly challenging to secure funding, directly impacting their cash flow and, consequently, their banking relationships.
Investor Behavior Shift
- Flight to Safety: Investors began favoring safer, higher-yielding investments over riskier startups.
- Decreased Startup Funding: The tech sector experienced a downturn, which led to fewer deposits at SVB.
🏃♂️ Customer Behavior and Bank Runs
As the news of SVB's precarious position spread, customer behavior shifted dramatically. Silicon Valley is a close-knit community, and the fear of insolvency prompted a rush to withdraw funds. This phenomenon marked a modern bank run, potentially fueled by social media and group communication.
With a staggering 90% of SVB's deposits exceeding the FDIC insurance limit, customers acted rationally, fearing they might not recover their funds. In a single day, $42 billion was withdrawn, leading to an irreversible crisis.
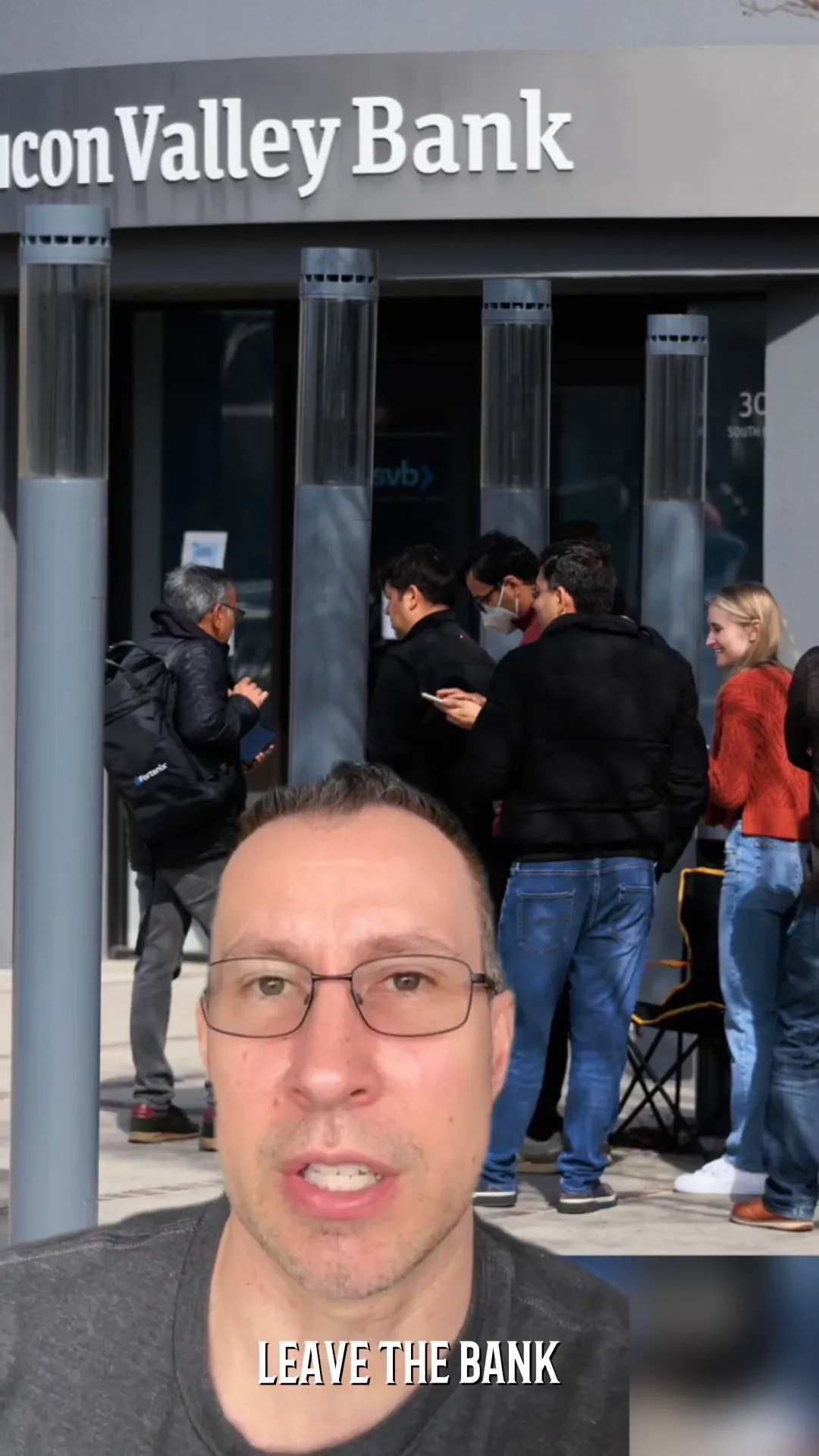

Modern Bank Runs
- Social Media Influence: The rapid spread of information through social media intensified customer fears and accelerated withdrawal rates.
- Trust Erosion: Once trust in the bank eroded, it became challenging for SVB to regain confidence among its customers.
🔍 Regulatory Oversight and Changes
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank raises significant questions about regulatory oversight. In the wake of the 2008 financial crisis, the Dodd-Frank Act was implemented to introduce stricter regulations aimed at preventing such failures. However, over time, these regulations have been weakened due to lobbying efforts from banks.
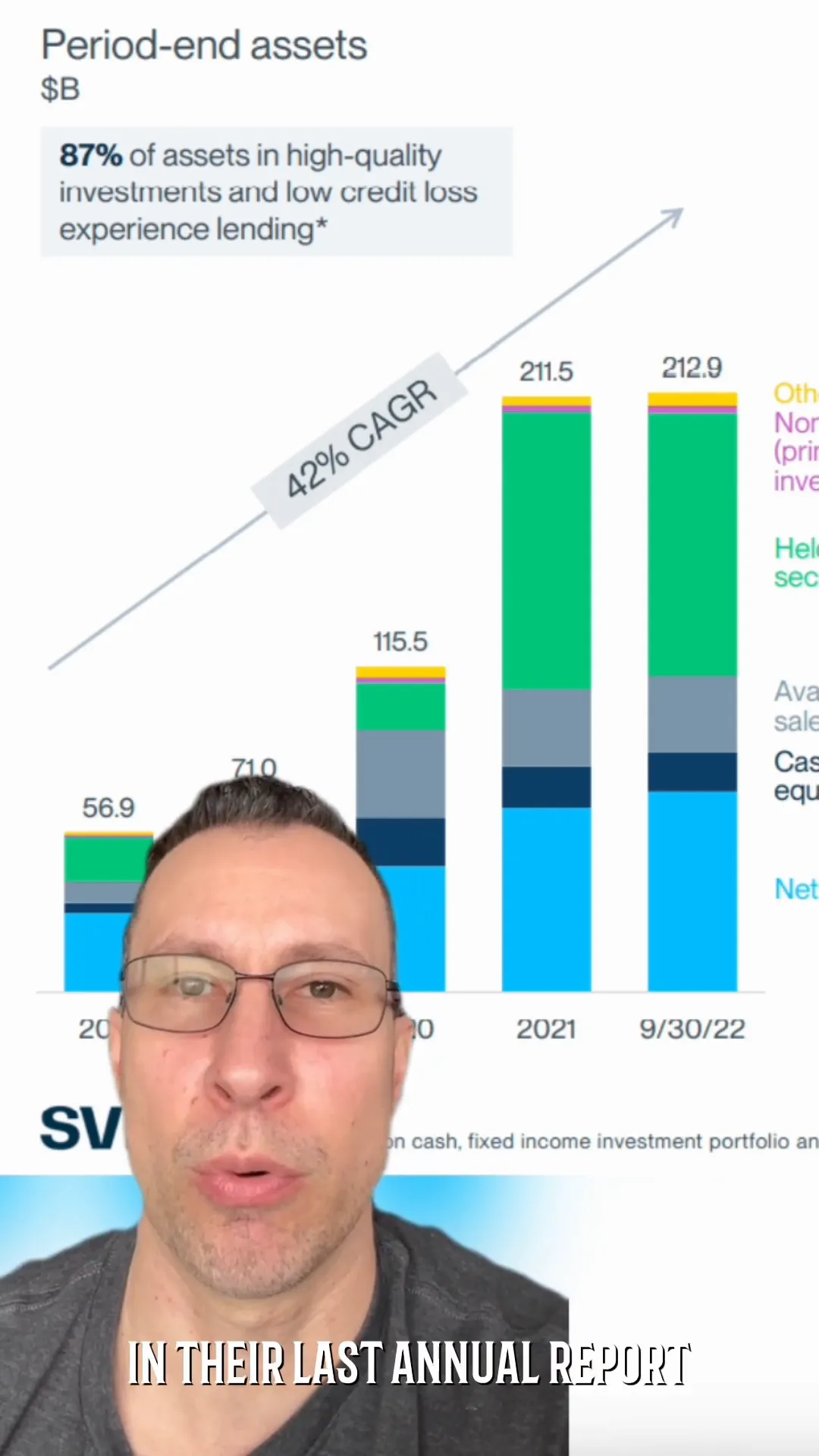
Initially, banks with assets over $50 billion were subjected to stringent rules. This threshold was later raised to $250 billion, allowing many institutions, including Silicon Valley Bank, to operate under less scrutiny. This change in classification meant that SVB, with its $212 billion in assets, was considered medium-sized for regulatory purposes and faced less rigorous oversight.
Consequences of Regulatory Changes
- Less Oversight: The reduction in regulatory scrutiny contributed to SVB's inability to manage risks effectively.
- Increased Vulnerability: With less oversight, banks like SVB became more susceptible to market shifts, particularly in volatile sectors like tech.
📜 The Role of the Dodd-Frank Act
The Dodd-Frank Act was a response to the reckless behaviors that led to the 2008 financial crisis. It aimed to increase transparency and accountability within the banking system. However, as regulations were rolled back, the effectiveness of the Dodd-Frank provisions diminished.
One significant aspect of the Dodd-Frank Act was the requirement for stress testing. These tests were designed to evaluate a bank's resilience to economic shocks. Unfortunately, the tests did not account for the rising interest rates that ultimately affected Silicon Valley Bank.

Impact of the Dodd-Frank Act on Silicon Valley Bank
- Regulatory Laxity: The shift in regulatory definitions allowed SVB to operate with less oversight, which may have contributed to its downfall.
- Stress Test Limitations: The lack of testing for rising interest rates left SVB unprepared for the economic shifts that ensued.
🔄 Stress Tests and Their Implications
Stress tests are meant to simulate adverse economic conditions to assess a bank's stability. These tests evaluate how well a bank can withstand financial shocks, including sudden interest rate increases. However, the failure to include rising interest rates in SVB's stress tests proved detrimental.
In 2022, stress tests focused on scenarios such as high unemployment and collapsing asset prices, but they overlooked the possibility of rising interest rates. This oversight directly impacted SVB's ability to navigate the financial landscape effectively.

Importance of Comprehensive Stress Testing
- Risk Management: Comprehensive stress tests should encompass a variety of economic scenarios, including interest rate fluctuations.
- Proactive Measures: Accurate stress testing can help banks identify vulnerabilities and implement strategies to mitigate risks.
🏦 The FDIC's Intervention
When Silicon Valley Bank faced an unprecedented crisis, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) stepped in to protect depositors. The FDIC's intervention aimed to restore confidence in the banking system and prevent a broader financial panic.
By ensuring that all deposits were covered, the FDIC acted swiftly to contain the situation, which could have spiraled out of control. This intervention highlighted the importance of regulatory bodies in maintaining stability during financial crises.

Role of the FDIC During Crises
- Deposit Protection: The FDIC guarantees deposits up to $250,000, providing a safety net for customers.
- Stabilizing Influence: By intervening during crises, the FDIC helps to restore trust in the banking system.
❓ FAQs About Silicon Valley Bank
As the fallout from the Silicon Valley Bank collapse continues, many questions arise regarding its implications and the future of banking. Here are some frequently asked questions:
What caused the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank?
The collapse was primarily due to poor risk management, a significant mismatch between long-term investments and short-term liabilities, and a rapid withdrawal of deposits triggered by customer fears.
How did rising interest rates affect SVB?
Rising interest rates devalued SVB's long-term investments, leading to financial instability and a significant drop in customer deposits as startups struggled to secure funding.
What is the Dodd-Frank Act?
The Dodd-Frank Act is a U.S. federal law that was enacted in response to the 2008 financial crisis, aiming to promote financial stability by implementing stricter regulations on banks.
What role did the FDIC play in the crisis?
The FDIC intervened to ensure that all deposits were covered, helping to prevent a broader panic and restore confidence in the banking system.
What can be learned from SVB's failure?
The failure of Silicon Valley Bank highlights the critical need for robust risk management practices, comprehensive regulatory oversight, and the importance of including various economic scenarios in stress testing.
Categories
- All Blogs (314)
- Client Testimonials (19)
- East Palo Alto (81)
- Graeham Watts Home Tours (23)
- Home Buyer's Process (34)
- Home Tours (28)
- Houses for sale in East Palo Alto (13)
- Investing (18)
- Landlord and Tenant Info (9)
- Menlo Park (49)
- Personal (5)
- Real Estate Questions Answered (91)
- Real Estate Tips (86)
- Redwood City (85)
- San Mateo County (10)
- Seller's Process (22)
Recent Posts







GET MORE INFORMATION

